The Hidden AI Security Gap Putting Businesses at Risk
AI is changing how businesses work. From marketing tasks to fraud detection, AI now drives daily operations. Yet security often gets overlooked. Most false

With the rise of cyber threats and data breaches, businesses need a proactive, multi-layered approach to security. iCorps delivers advanced cybersecurity and data privacy protection, ensuring your IT environment stays secure, compliant, and resilient against evolving threats.

Next-Gen Firewall with Unified Threat Management

Next-Gen Firewall with Unified Threat Management
.png?width=196&height=214&name=Group%201000005398%20(1).png)
Intrusion Detection & Prevention
.png?width=196&height=214&name=Group%201000005398%20(1).png)
Intrusion Detection & Prevention
.png?width=196&height=214&name=Group%201000005398%20(2).png)
Advanced EDR for Endpoint, Cloud & SaaS Security
.png?width=196&height=214&name=Group%201000005398%20(2).png)
Advanced EDR for Endpoint, Cloud & SaaS Security
.png?width=196&height=215&name=Group%201000005398%20(3).png)
Email Threat Management Gateway
.png?width=196&height=215&name=Group%201000005398%20(3).png)
Email Threat Management Gateway
.png?width=196&height=215&name=Group%201000005398%20(4).png)
DNS Firewall: Stop Threats Before They Start
.png?width=196&height=215&name=Group%201000005398%20(4).png)
DNS Firewall: Stop Threats Before They Start
.png?width=196&height=215&name=Group%201000005398%20(5).png)
Identity Management: Protecting User Identity
.png?width=196&height=215&name=Group%201000005398%20(5).png)
Identity Management: Protecting User Identity
Empower your business with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)—ensuring secure, identity-based access to apps and data, no matter where users connect from.
Never trust, always verify. Secure every connection.

.png?width=100&height=101&name=Frame%20(1).png)
.png?width=100&height=101&name=Frame%20(2).png)
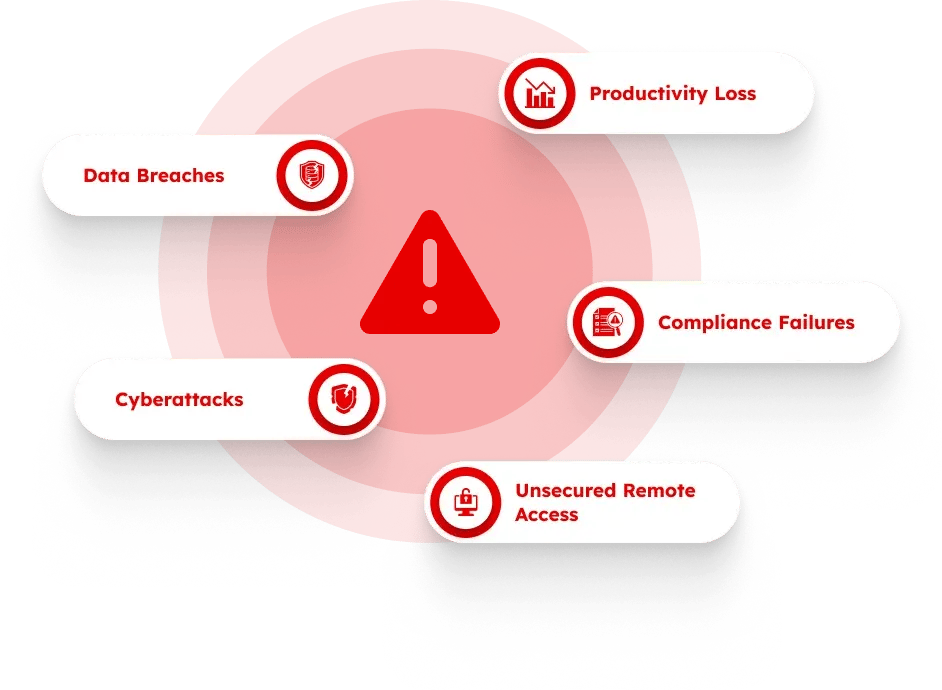

Managed network security provides the expertise, hardware, software, installation, configuration, ongoing patch management, and continuous updates to keep your network safe. With managed network security, you have access to a team of advanced security specialists and layered services such as:
For businesses of all sizes, iCorps managed security service provides enterprise protection for a fraction of the cost of equivalent internal systems. Our security experts can define security policies and access privileges, from online and mobile endpoints to wireless support and VPN access. As your business changes, our experts will collaboratively fine-tune your security monitoring and policies to ensure your business has the highest level of network protection. Comprehensive reports keep you informed of your current security status and provide insight into:

AI is changing how businesses work. From marketing tasks to fraud detection, AI now drives daily operations. Yet security often gets overlooked. Most false

For many small and mid-sized organizations, AI governance still sounds like something reserved for large enterprises with legal teams and compliance false

As artificial intelligence becomes more accessible, many business leaders wrestle with a familiar dilemma. Should we hire more people or invest in false